Learn about the oral health precautions that are taken to prevent cross-infection during dental procedures
The dental profession has always taken precautions to prevent cross-infection. Indeed, with new knowledge and better technology, the dental procedures to prevent infection have become even more stringent.
So now, more than ever, the possibility of getting infected while undergoing dental treatments are practically NIL.
What Is Cross-Infection?
It is the transmission of diseases from one patient to another, or from the patient to the dentist, or vice-versa.
This is prevented by the routine practice of Universal Infection Control, so described because it is practised for ALL patients who walk into the dental clinic.
Universal Infection Control routines involve a range of dental procedures such as: -
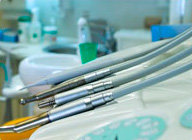 Sterilisation
Sterilisation
All equipment for dental treatments and dental procedures that has been used are thoroughly washed and then sterilised. Sterilisation involves the use of heat, chemicals or radiation to destroy all germs.
The most common steriliser used is the autoclave.
All instruments such as
- tweezers, mouth mirrors and numerous other hand instruments
- burs (the small drill bits that do the cutting of the tooth)
- metals cups
- trays on which the instruments are placed
- the modern dental handpiece (drill)
and all other instruments placed in the mouth would have been sterilised before your dental treatment.
The Use of Disposables
In dental clinics, many items are used only once and then thrown away.
These include:
- injection needles saliva ejectors (suction tips)
- scalpel blades napkins, towels, cups
Barriers
Your dentist routinely wears gloves, masks, goggles or face shields during treatment. These serve as protective barriers against the transmission of diseases. Gloves are disposed of after each patient.
 Chemical Disinfectants
Chemical Disinfectants
After every treatment, while the dentist is washing his / her hands with antiseptic soap, the nurse would ensure that the dental chair and table surfaces which are contaminated are wiped with disinfectants.
Disposal of Waste
To further protect you from accidental contamination, used articles such as needles, gloves and gauze are considered as biohazardous and are collected in separate bins and disinfected or disposed of, separately from normal refuse.
Download the Healthhub app on Google Play or Apple Store to access more health and wellness advice at your fingertips.

HealthHub AI